MegaPose
6D Pose Estimation of Novel Objects via Render & Compare
CoRL 2022

Overview
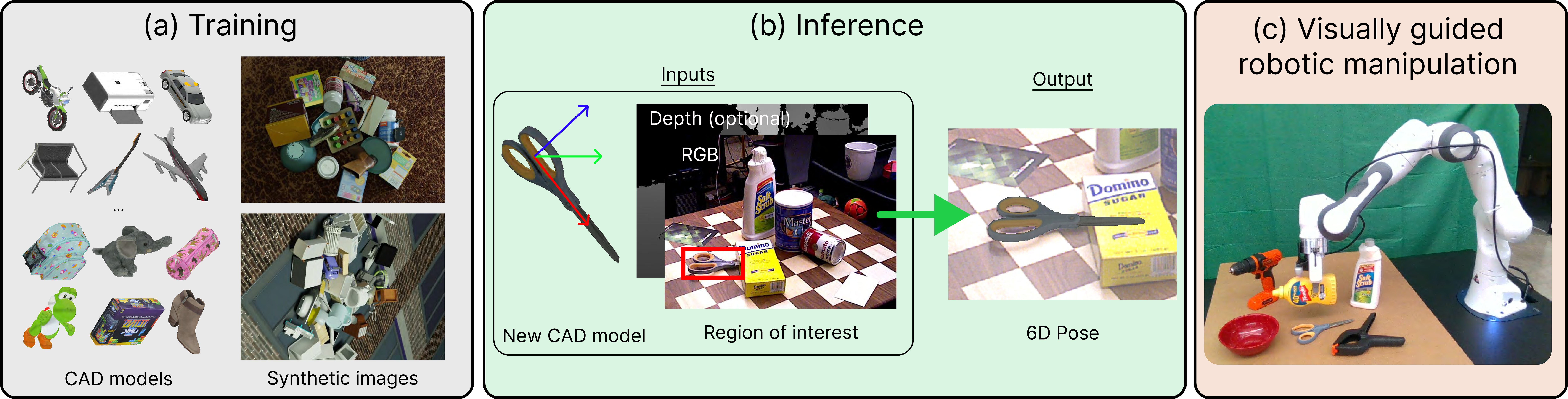
MegaPose is a 6D pose estimation approach (a) that is trained on millions of synthetic scenes with thousands of different objects and (b) can be applied without re-training to estimate the pose of any novel object, given a CAD model and a region of interest displaying the object. It can thus be used to rapidly deploy visually guided robotic manipulation systems in novel scenes containing novel objects (c).
1 min presentation video
Abstract
We introduce MegaPose, a method to estimate the 6D pose of novel objects, that is, objects unseen during training. At inference time, the method only assumes knowledge of (i) a region of interest displaying the object in the image and (ii) a CAD model of the observed object. The contributions of this work are threefold. First, we present a 6D pose refiner based on a render & compare strategy which can be applied to novel objects. The shape and coordinate system of the novel object are provided as inputs to the network by rendering multiple synthetic views of the object's CAD model. Second, we introduce a novel approach for coarse pose estimation which leverages a network trained to classify whether the pose error between a synthetic rendering and an observed image of the same object can be corrected by the refiner. Third, we introduce a large scale synthetic dataset of photorealistic images of thousands of objects with diverse visual and shape properties, and show that this diversity is crucial to obtain good generalization performance on novel objects. We train our approach on this large synthetic dataset and apply it without retraining to hundreds of novel objects in real images from several pose estimation benchmarks. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on the ModelNet and YCB-Video datasets. An extensive evaluation on the 7 core datasets of the BOP challenge demonstrates that our approach achieves performance competitive with existing approaches that require access to the target objects during training. Code, dataset and trained models are made available.
Method
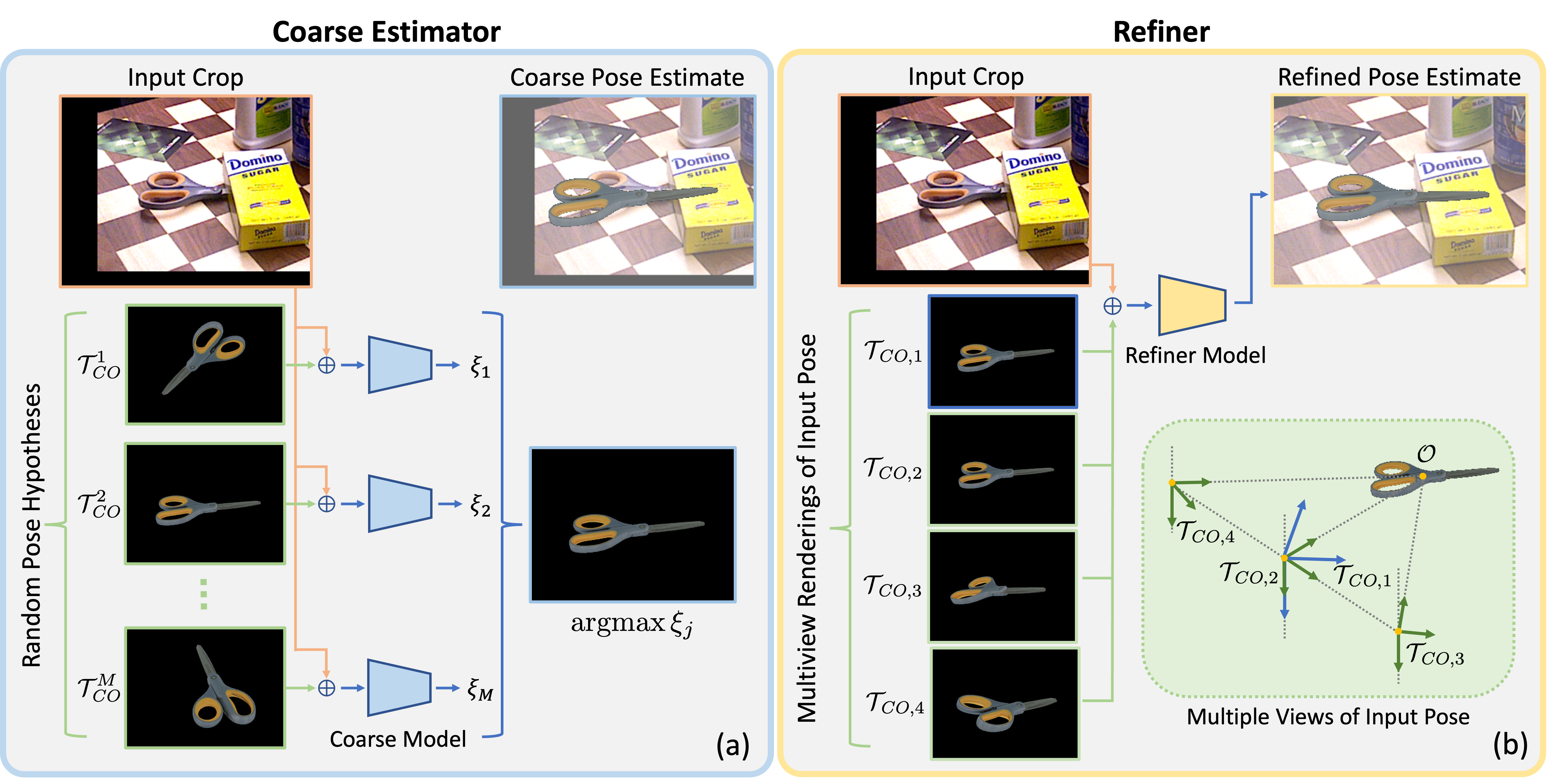
\(\oplus\) denotes concatenation. (a) Coarse Estimator: Given a cropped input image the coarse module renders the object in multiple input poses \(\{\mathcal{T}_{CO}^j\}\). The coarse network then classifies which rendered image best matches the observed image. (b) Refiner: Given an initial pose estimate \(\mathcal{T}_{CO}^k\) the refiner renders the objects at the estimated pose \(\mathcal{T}_{\textit{CO},1} := \mathcal{T}_{CO}^k\) (blue axes) along with 3 additional viewpoints \(\{\mathcal{T}_{\textit{CO},i}\}_{i=2}^4\) (green axes) defined such that the camera \(z\)-axis intersects the anchor point \(\mathcal{O}\). The refiner network consumes the concatenation of the observed and rendered images and predicts an updated pose estimate \(\mathcal{T}_{CO}^{k+1}\).
Qualitative results
Video
Results on the BOP datasets
For each example, we show (from left to right) (i) the input region of interest (ii) the coarse estimate, and (iii) the refined poses.Tracking results
In the first frame we run the complete megapose pose estimation pipeline consisting of (i) detection (ii) coarse estimation and (iii) multiple refinement steps (5 in this case). In subsequent frames we run a single pose refinement step using the previous pose estimate as the initialization.Robotic grasping experiments
In each video the robot attempts to grasp a specific target object (e.g. bleach bottle). The robot (i) moves back to capture an RGB image, (ii) estimates the pose of the target object and (iii) executes a specific grasp that has been annotated for each target object. We allow the robot to rotate the grasp by 180 degrees to ease kinematic reachability.Using MegaPose
6D pose estimation of novel objects
You can try MegaPose using the 3D models of your own objects! We provide a notebook for running pose estimation on new objects in the github repository.
Large-scale synthetic dataset
We release the large-scale synthetic training dataset we used to train MegaPose. You can use it for your own task! Please see the github repository for usage.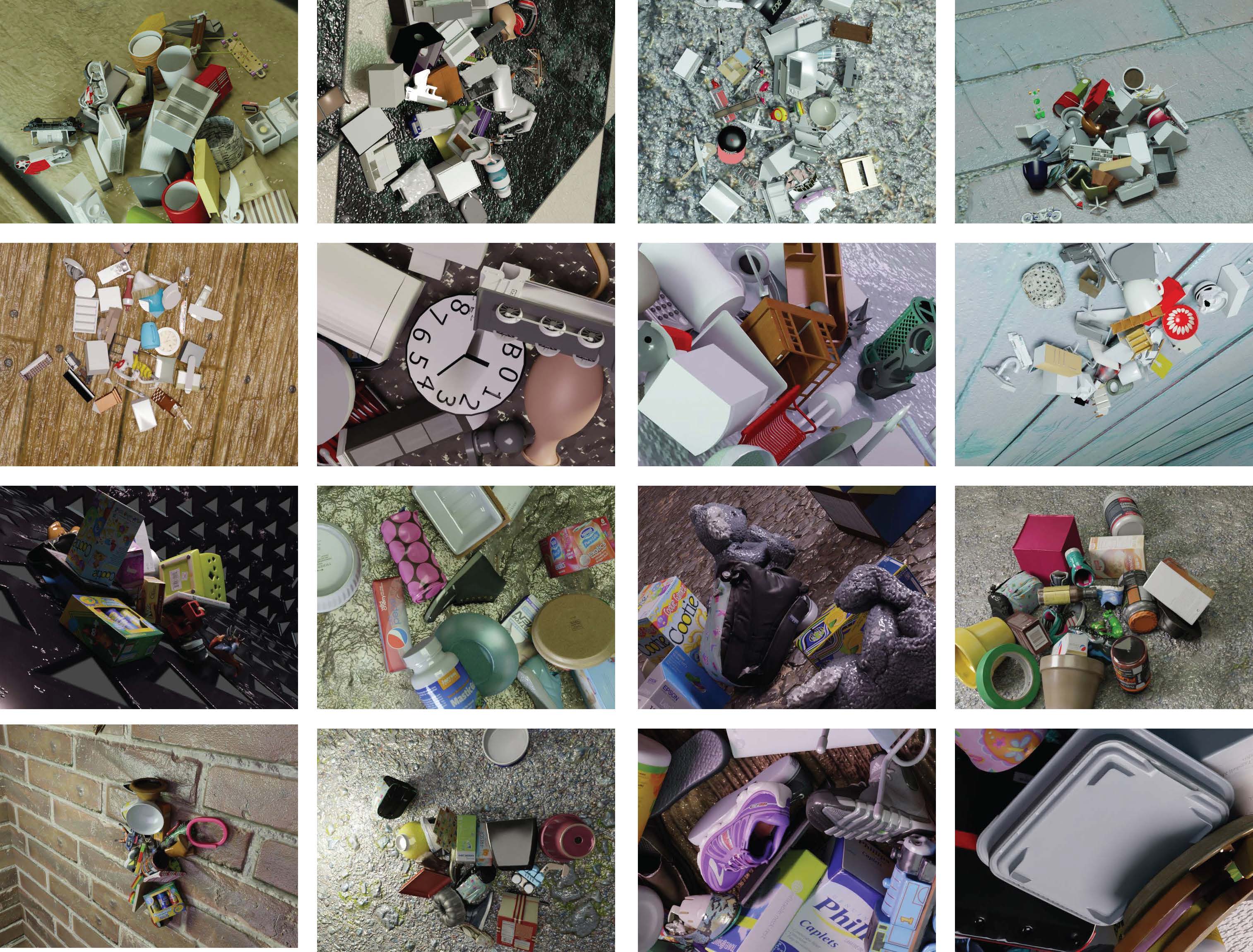
BibTeX
@inproceedings{labbe2022megapose,
title = {MegaPose: 6D Pose Estimation of Novel Objects via Render \& Compare},
author = {Labb\'e, Yann and Manuelli, Lucas and Mousavian, Arsalan and Tyree, Stephen and Birchfield, Stan and Tremblay, Jonathan and Carpentier, Justin and Aubry, Mathieu and Fox, Dieter and Sivic, Josef},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 6th Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL)},
year = {2022},
} 








